[CVPR 2022] High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models
摘要
By decomposing the image formation process into a sequential application of denoising autoencoders, diffusion models (DMs) achieve state-of-the-art synthesis results on image data and beyond. Additionally, their formulation allows for a guiding mechanism to control the image generation process without retraining. However, since these models typically operate directly in pixel space, optimization of powerful DMs often consumes hundreds of GPU days and inference is expensive due to sequential evaluations. To enable DM training on limited computational resources while retaining their quality and flexibility, we apply them in the latent space of powerful pretrained autoencoders. In contrast to previous work, training diffusion models on such a representation allows for the first time to reach a near-optimal point between complexity reduction and detail preservation, greatly boosting visual fidelity. By introducing cross-attention layers into the model architecture, we turn diffusion models into powerful and flexible generators for general conditioning inputs such as text or bounding boxes and high-resolution synthesis becomes possible in a convolutional manner. Our latent diffusion models (LDMs) achieve new state of the art scores for image inpainting and class-conditional image synthesis and highly competitive performance on various tasks, including unconditional image generation, text-to-image synthesis, and super-resolution, while significantly reducing computational requirements compared to pixel-based DMs.
研究动机与主要贡献
主要问题
- 基于 GAN 的生成模型可以很好地采样出感知质量(语义质量)很好的高分辨率图像,但优化起来成本很高,而且多样性较差,不能很好地捕捉全面的概率分布
- VQVAE、VQGAN 等其它似然模型可以实现较好的密度估计,但是采样质量不如 GAN 模型
- Autoregressive 模型由于序列性质的结构,需要较大的计算量和时间成本,因此只能限制于低分辨率采样
- 近期,扩散模型在密度估计和采样质量上都取得了 SOTA 效果,但直接在像素空间进行扩散过程会导致较低的推理速度以及高昂的训练成本
作者提出,几乎所有基于似然的生成模型都分为两个阶段:
- 感知压缩阶段(Perceptual Compression Stage):移除图像中的高频细节,但是仍然学习到少量的语义信息
- 语义压缩阶段(Semantic Compression Stage):生成模型学习图像语义以及数据的组成概念
本篇工作主要从感知压缩阶段出发,试图找到一个具有一定的感知能力,但是计算量更合适的空间,来训练 Diffusion Model,以克服目前的 Diffusion Models 存在的缺点
主要贡献
- 提出在隐空间(Latent Space)中训练 Diffusion Model,在计算量和细节保真度的平衡之间找到更优解
- 引入交叉注意力(Cross Attention),使降噪模型可以以文字等其它模态的信息作为条件进行多模态预测噪声
主要方法与模型结构
图像压缩模型(感知压缩)
感知压缩本质上是一个在计算量和细节保真度之间的 tradeoff,之前的 Diffusion Model 在像素空间上训练模型,如果期望模型可以采样出一张分辨率很高的图片,需要在高维的空间中训练模型,训练和推理的计算成本和时间成本都很高昂。引入感知压缩就是通过 Autoencoder 对原图片进行处理,忽略掉图片中的高频信息,只保留重要、基础的一些特征。这种方法带来的的好处能够大幅降低训练和采样阶段的计算复杂度,大大降低了文生图等任务的落地门槛。
感知压缩主要利用一个预训练的自编码模型,该模型能够学习到一个在感知上等同于图像像素空间的潜在表示空间(Latent Space)。这种方法的一个优势是只需要训练一个通用的自编码模型,就可以用于不同的扩散模型的训练,在不同的任务上使用。
文章提出的基于感知压缩的 Diffusion Model 是一个两阶段训练的过程,第一阶段需要训练一个 Autoencoder,第二阶段才需要训练扩散模型本身。
在第一阶段训练自编码器时,为了避免潜在表示空间出现高度的异化,文章提出了两种正则化放啊,一种是 KL-rrg(类似于 VAE),另一种是 VQ-reg(类似于 VQGAN)。在官方发布的一阶段预训练模型中,会看到 KL 和 VQ 两种实现。在 Stable Diffusion 中主要采用 AutoencoderKL 这种实现。
采样因子
具体来说,给定图像 ,模型首��先利用一个编码器 来将图像编码到潜在表示空间 ,其中 ,然后再用解码器从潜在表示空间重建图片 。在感知压缩压缩的过程中,下采样因子的大小为 ,它是 2 的次方,即 。
隐空间的扩散模型
在像素空间的普通 Diffusion Model 可以解释为一个时序去噪自编码器(equally weighted sequence of denoising autoencoders), ,其目标是根据输入 去预测一个对应去噪后的变体,即预测噪音,其中 是输入 的加噪版本。相应的目标函数可以写成如下形式:
其中, 从 中均匀采样获得。
而在 LDM 中,引入了预训练的感知压缩模型,它包括一个编码器 和一个解码器 。这样在训练时就可以利用编码器得到 ,从而让扩散模型在潜在表示空间中学习,通过降噪得到图像在隐空间的表示,最终再通过解码器恢复到像素空间。在维度较低的隐空间中进行扩散训练实现了较低的计算量。相应的目标函数可以写成如下形式:
条件机制:Cross Attention
文章通过对普通的 LDM 进行拓展得到条件时序去噪自编码器(conditional denoising autoencoder) 来实现多模态的条件生成,其中 作为条件来控制图片合成的过程。
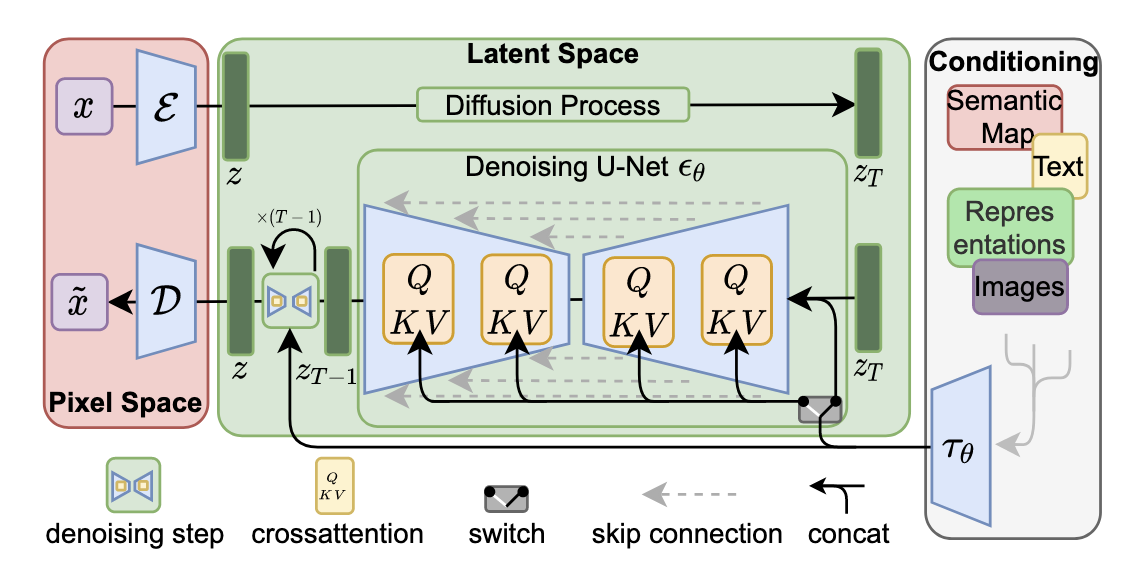
具体来说,论文通过在 UNet 主干网络上增加交叉注意力机制(Cross Attention)来实现。为了能够从多个不同的模态获得 ,本文引入了一个领域特定的编码器(domain specific encoder),它用来将 映射为一个中间表示 ,便于引入各种模态的条件(文本、类别、layout 等)。最终模型就可以通过一个 Cross Attention 层映射将控制信息融入到 UNet 的中间层,Cross Attention 实现如下:
其中,
其中 是 UNet 的一个中间表示。相应的目标函数可以写成如下形式:
实验
感知压缩
采样因子 的大小为 ,如果 就是在像素空间进行扩散过程的特殊情况。如果 越大,则信息压缩越严重,可能会噪声图片失真,但同时训练资源占用的也越少。文章对比了 在分别 下的效果,发现 在 之间可以比较好的平衡压缩效率与视觉感知效果。作者重点推荐了 LDM-4 和 LDM-8。
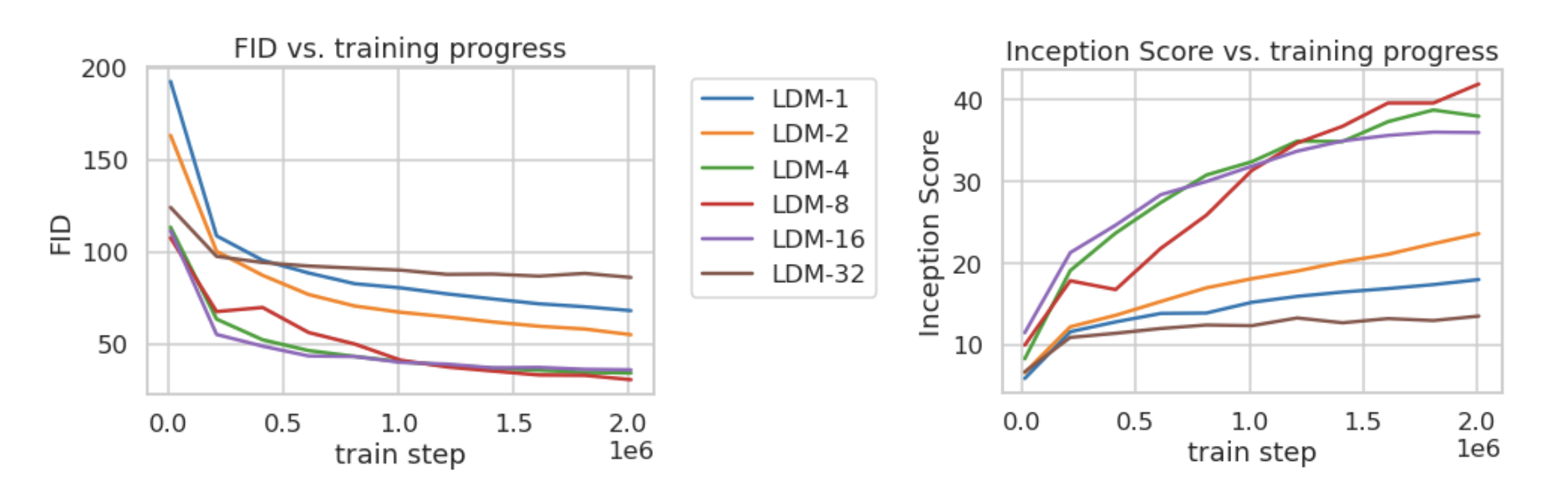
值得注意的是,Stable Diffusion v2-1 常用的下采样因子是 8,而 Stable Cascade 的下采样可高达 42,将 的图像压缩至 进行扩散过程。