Visual Autoregressive Modeling: Scalable Image Generation via Next-Scale Prediction
摘要
We present Visual AutoRegressive modeling (VAR), a new generation paradigm that redefines the autoregressive learning on images as coarse-to-fine “next-scale prediction” or “next-resolution prediction”, diverging from the standard raster-scan “next-token prediction”. This simple, intuitive methodology allows autoregressive (AR) transformers to learn visual distributions fast and can generalize well: VAR, for the first time, makes GPT-style AR models surpass diffusion transformers in image generation. On ImageNet 256×256 benchmark, VAR significantly improve AR baseline by improving Fréchet inception distance (FID) from 18.65 to 1.73, inception score (IS) from 80.4 to 350.2, with 20× faster inference speed. It is also empirically verified that VAR outperforms the Diffusion Transformer (DiT) in multiple dimensions including image quality, inference speed, data efficiency, and scalability. Scaling up VAR models exhibits clear power-law scaling laws similar to those observed in LLMs, with linear correlation coefficients near −0.998 as solid evidence. VAR further showcases zero-shot generalization ability in downstream tasks including image in-painting, out-painting, and editing. These results suggest VAR has initially emulated the two important properties of LLMs: Scaling Laws and zero-shot generalization. We have released all models and codes to promote the exploration of AR/VAR models for visual generation and unified learning.
研究背景与动机
通过回顾先前的视觉 Autoregressive 模型(即采用 next-token 范式进行生成),从 scaling laws 和性能的角度将其与 NLP 领域的 LLMs 进行比较,宏观上说明了传统视觉 AR 模型存在的问题。
- 传统视觉 AR 模型是否遵循 scaling laws 有待探索和验证
- 性能有待提升
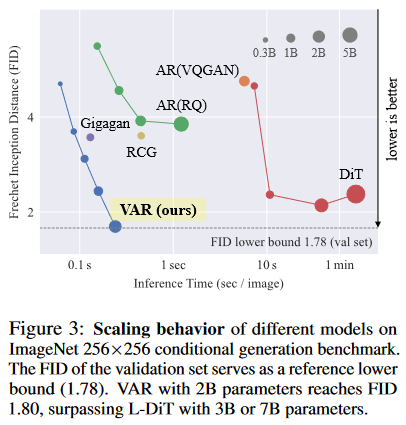
上图展示了传统 Visual AR 模型在 scaling laws 方面的局限性,并以 FID 作为评价指标,展示了性能效果方面的不足。
问题发现与提出
首先文章花费了大量篇幅来用数学语言描述以 next-token prediction 作为生成范式的传统视觉自回归模型的定义和流程,大致包括以下流程:
-
输入 raw image,Encoder 得到对应的 feature map。
-
输入feature map,Quantizer 得到对应的量化 image token。
在量化步骤,会将每个特征向量映射到与其在欧几里得意义上最接近的 Codebook 中的 code。
-
Decoder 通过接收在 Codebook 中查找得到的 生成重构的图像。
下图展示了传统 VAR 方法与本文提出的 VAR 方法的对比。其中图(a)展示了 NLP 领域的 next-token prediction,图(b)展示了上述公式定义的 next-image-token prediction 的过程,包含量化与展平的步骤,图(c)展示了本文提出的 next-scale prediction。
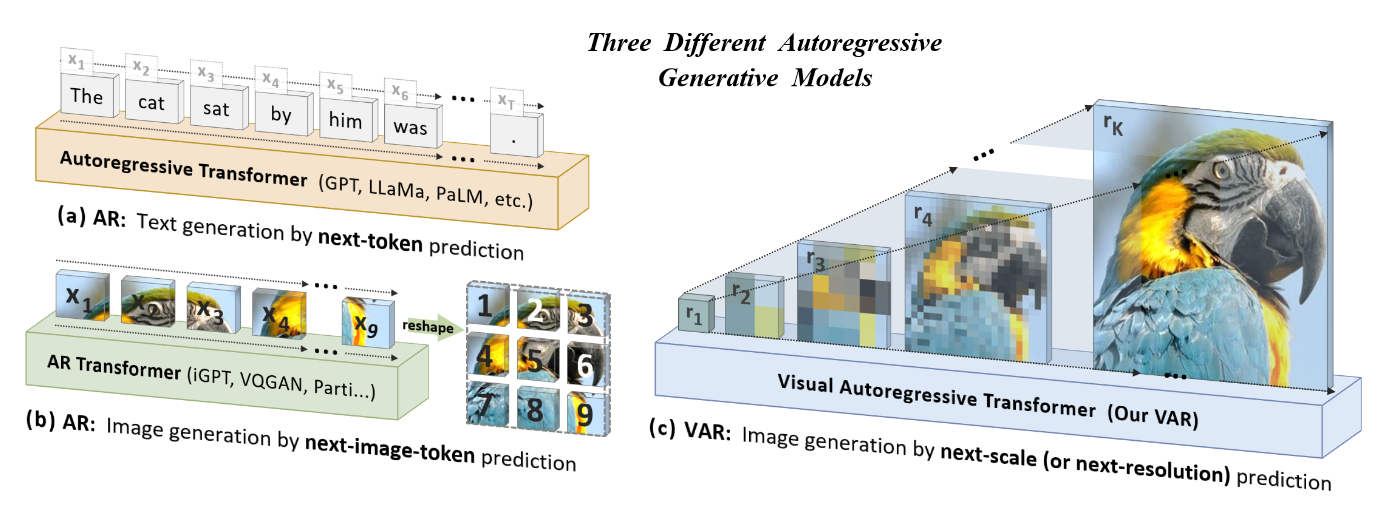
文章发现了目前传统 VAR 模型存在的三个问题。
-
VQGAN 违反了 Autoregressive 的数学前提。Autoregressive 模型假设当前时间步的 token 只取决于其之前时间步的 token 前缀 ,具有单向相关性(unidirectional)。而 VQGAN 中的 image encoder 直接从具有双向相关性(bidirectional)的 feature map 中进行量化和展平,因此得到的 image tokens 同样具有双向相关性,违反了数学假设。
作者在附录中检查了 VQGAN 模型在量化步骤之前的注意力层输出的图像注意力分数,证明了较强的双向相关性。
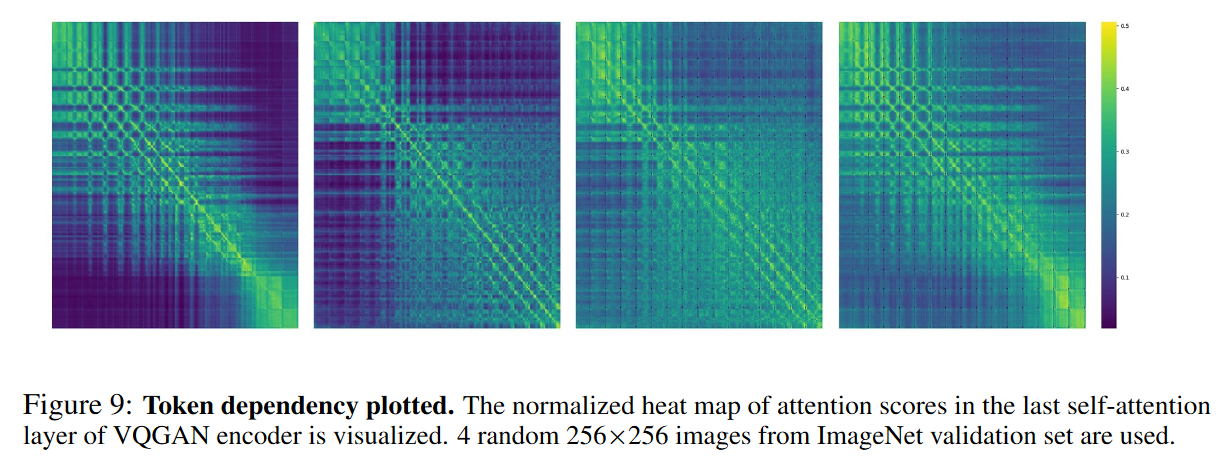
作者解释,这是因为在图像 VAE 以及其他类似的工作的自注意力层中,并没有使用任何注意力掩码机制,如 sequence mask 以及 causal attention 等,导致了双向相关性。
This is not surprising since the VQVAE model, trained to reconstruct images, leverages self-attention layers without any attention mask. Some work [67] has used causal attention in self-attention layers of a video VAE, but we did not find any image VAE work uses causal self-attention.
-
image tokens 的空间结构性被破坏。由于先前的 VAR 工作均是采用类似于先列后行的一维顺序存储 image tokens 并进行 Autoregressive 生成,image tokens 的扁平化破坏了图像特征图固有的空间局部性。
-
时间复杂度过高,影响生成效率。使用传统的视觉 Autoregressive 方法生成 的 token 序列,需要 的注意力步骤以及 的计算复杂度。
主要方法与贡献
主要方法
本文的工作重新考虑了以什么样的顺序生成图像。人类通常以分层的方式感知或创建图像,首先捕获全局结构,然后捕获局部细节。这种多尺度、由粗到精(coarse-to-fine)的方法很自然地给图像暗示了一种顺序。此外,受广泛使用的多尺度(multi-scale)设计工作的启发,本文将图像的自回归学习定义为下图展示的 next-scale prediction。
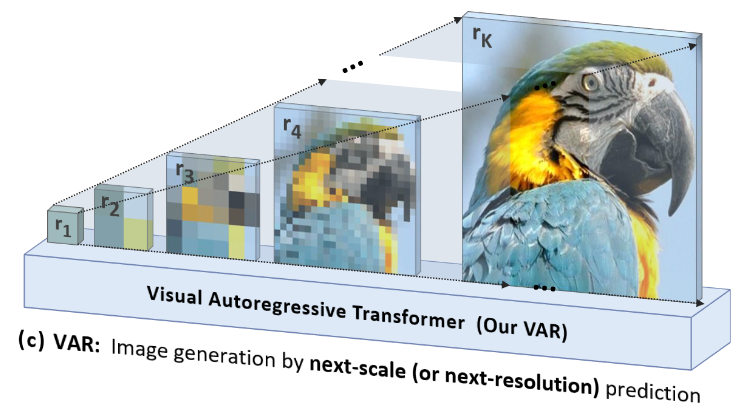
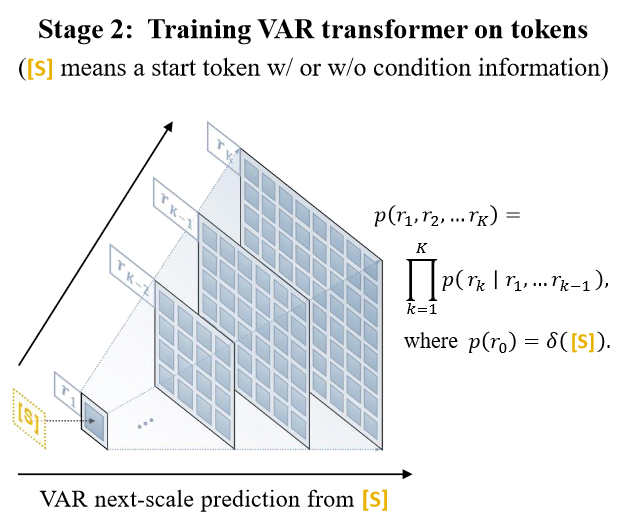
自回归过程从分辨率为 的 token map 开始,并逐步扩大分辨率:在每一步,Transformer 以之前生成的所有分辨率的 token maps 为条件预测下一大分辨率的 token map。
通过从 next-token prediction 策略转变为 next-scale prediction 策略,重新概念化了对图像的自回归建模。在这里,自回归单元是整个 token map,而不是传统方法的单个 token。先将特征图 量化为 个多尺度标记图 ,每个图的分辨率 逐步增加,最终达到 与原始特征图的分辨率 匹配。自回归似然性公式为:
其中每个自回归单元 是包含 个标记的第 个尺度的标记图,而序列 作为 的“前缀”。在第 个自回归步骤中,所有 中的 h_k \times w_k 标记的分布将并行生成,并以 的前缀和关联的第 个位置嵌入图为条件。如下图所示。
请注意,在 VAR 的训练中,使用逐块的因果注意力掩码,以确保每个 只能关注其前缀 ,从而满足 Autoregressive 模型的数学假设前提。
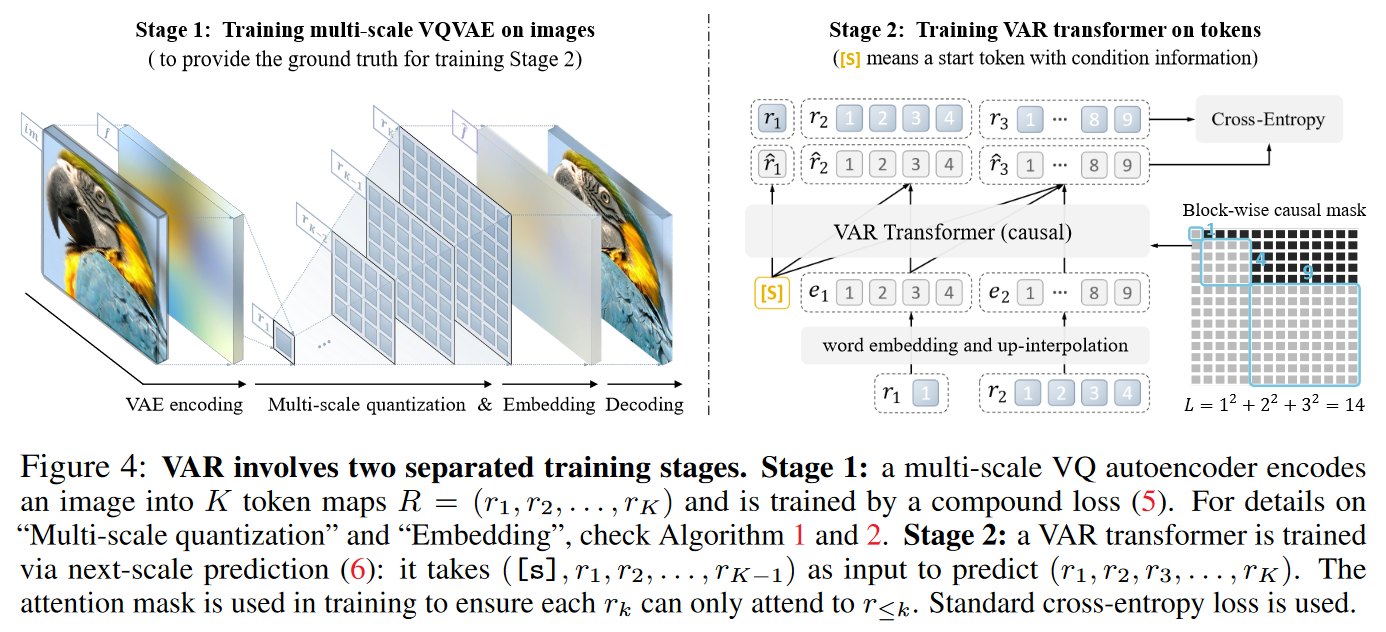
本文在结构上的主要贡献是开发了适用于 next-scale prediction 的 multi-scale VQ quantizer,同时结合新的 VQ quantizer 提出了新的图像自回归生成模型,并进一步论证了该方法展示出的与 LLMs 类似的 scaling laws 能力。
模型主要结构
Multi-scale VQ quantizer
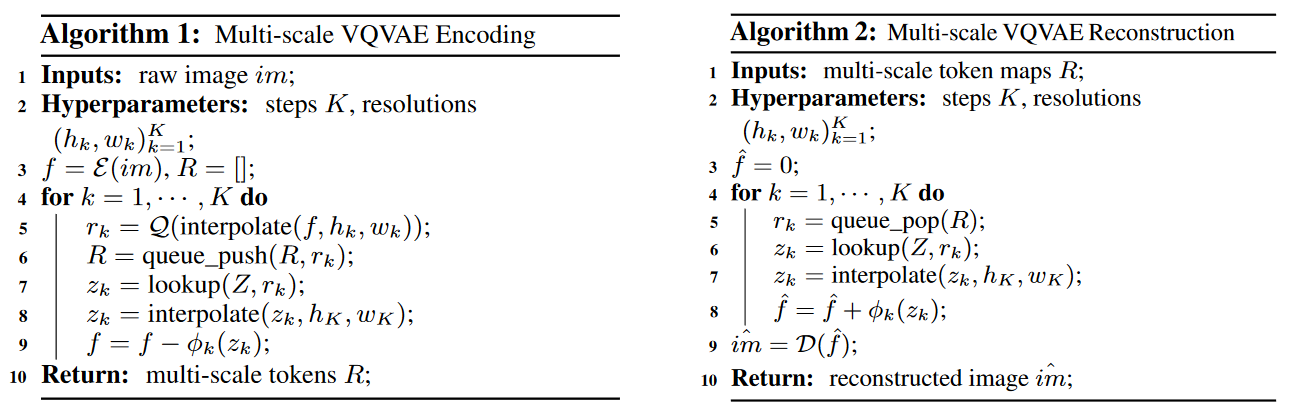
首先,需要设计一个满足多尺度要求的 VQ tokenizer,作者使用了与 VQVAE 相同的框架,并采用了改进的多尺度量化层,并加入了对 feature map 的残差设计:对 encoder 输出的 feature map 进行 interpolate 构建不同尺度的 feature map,不同 feature map 之间通过计算残差的方式进行连接,并结合 quantizer 得到离散序列。VQ quantizer(VAR tokenizer)的具体算法如下图所示。
VAR Transformer
作者将重点放在了 VAR tokenizer 的理念和设计上,在 VAR Transformer 中保持了与 GPT-2 和 VQGAN 相同的简洁设计,在结构设计上只融合了 adaptive normalization(AdaLN)。
在训练完 VQ tokenizer 后,需要在离散化后的序列上训练生成模型,上图中 分别表示不同尺度的离散序列。作者将传统的单向自回归模型修改为双向与单向混合的模式,同一个尺度的图片内部使用双向 attention,token 彼此可见,不同尺度的图片之间使用单向 attention ,具有从粗粒度到细粒度的 causal dependency,保证了满足 Autoregressive 假设的数学前提。
单个尺度的图片可以一步生成,生成所需的迭代步数取决于 VQ tokenizer 设计的尺度层数 。
总结
本文主要从视觉 Autoregressive 模型生成图像像素的顺序出发,重新思考,通过人类感知图像的方式设计了 next-scale 的生成范式,每一步迭代生成一张完整的图像,但生成图像的分辨率逐步提升,最终得到高像素目标图像。
对文章开篇提出的问题的解决:
- 使用 causal attention 对自注意力进行掩码,从而满足 Autoregressive 模型对时间序列的数学假设。
- 在 quantization 步骤使用二维的方式存储整个 image token map,保证了结构的完整性。
- 得益于多尺度思想的生成方式,时间复杂度和计算开销显著降低。以生成 个 image tokens 为例,传统的视觉 Autoregressive 生成需要 次解码迭代和 次总计算。相比之下,本文提出的 VAR 只需要 次迭代和 次总计算量。
文章还论证了 VAR 模型展现出的与 LLMs 相同的 scaling laws 能力。