MARS: Mixture of Auto-Regressive Models for Fine-grained Text-to-image Synthesis
摘要
Auto-regressive models have made significant progress in the realm of language generation, yet do not perform on par with diffusion models in the domain of image synthesis. In this work, we introduce MARS, a novel framework for T2I generation that incorporates a specially designed Semantic Vision-Language Integration Expert (SemVIE). This innovative component integrates pre-trained LLMs by independently processing linguistic and visual information—freezing the textual component while fine-tuning the visual component. This methodology preserves the NLP capabilities of LLMs while imbuing them with exceptional visual understanding. Building upon the powerful base of the pre-trained Qwen-7B, MARS stands out with its bilingual generative capabilities corresponding to both English and Chinese language prompts and the capacity for joint image and text generation. The flexibility of this framework lends itself to migration towards any-to-any task adaptability. Furthermore, MARS employs a multi-stage training strategy that first establishes robust image-text alignment through complementary bidirectional tasks and subsequently concentrates on refining the T2I generation process, significantly augmenting text-image synchrony and the granularity of image details. Notably, MARS requires only 9% of the GPU days needed by SD1.5, yet it achieves remarkable results across a variety of benchmarks, illustrating the training efficiency and the potential for swift deployment in various applications. Code will be available at https://github.com/fusiming3/MARS.
自回归模型在语言生成领域取得了显著进展,但在图像合成领域的表现却不如扩散模型。本文介绍了 MARS 方法,一种用于文本到图像生成的新框架。
-
该框架结合了专门设计的语言-视觉语言集成专家(Semantic Vision-Language Integration Expert,SemVIE)。通过独立处理语言和视觉信息来整合预训练的 LLM,冻结语言部分的同时微调视觉部分。
这种方法保留了 LLM 的自然语言处理能力,同时赋予其卓越的视觉理解能力。
-
基于强大的预训练模型 Qwen-7B,MARS 在生成能力上脱颖而出,能够处理汉英双语的 T2I 生成任务,并具备联合图像和文本生成的能力。
-
此外,MARS 采用了多阶段训练策略,首先通过互补的双向任务建立强大的图文对齐,然后专注于精细化文本到图像的生成过程,显著提高了文本和图像的同步性和图像细节的细腻程度。
-
值得注意的是,MARS 的训练仅需 Stable Diffusion v1-5 训练所需 GPU 天数的 9%,同时在各种基准测试中取得了显著成果,展示了训练效率和在各种应用中快速部署的潜力。
主要方法与模型结构
总体结构
MARS 是一个将大语言模型(LLM)与视觉生成能力结合在统一框架内的创新系统,体现了一种平衡的多模态架构,包含了独特但协调一致的视觉和语言专家模型,如下图所示。
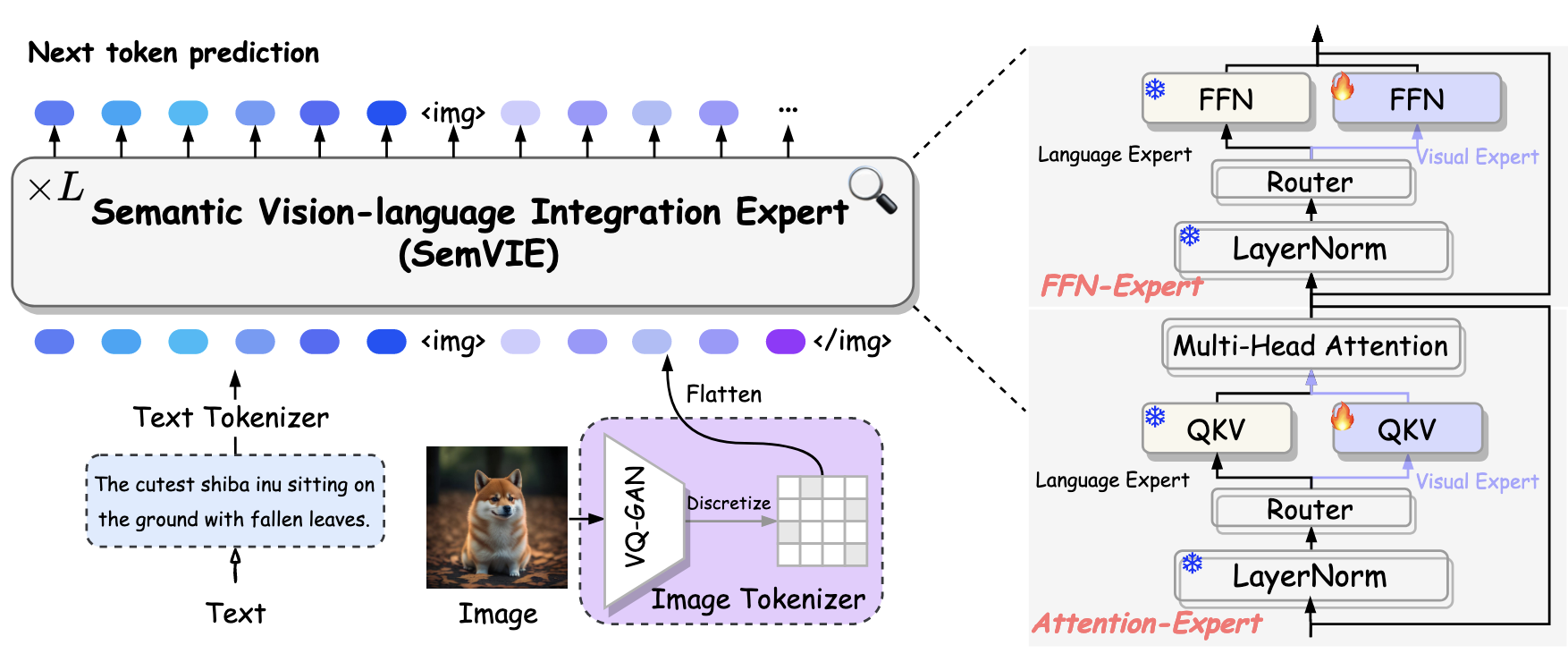
语义视觉-语言集成专家
分词(Tokenization)
在本研究中,预训练的 LLM Qwen-7B 作为基础语言框架,利用其分词器将文本数据拆解为一系列代表性 tokens。同时,在视觉模态中,使用受 VQ-GAN 架构启发的编码器将图像转换为特征图,其中,预定义为量化参数 16,D 表示特征维度。特征图随后使用视觉码本 VQ-GAN 进行量化,将其映射为一系列离散的代码索引 。这个过程有效地将 256×256 像素的图像重构为一系列 256 个 token,其中每个 token 代表 16×16 像素的图像段。值得注意的是,视觉码本由 8192 个唯一编码组成。
在 MARS 的词汇表中,这些视觉组件与传统的文本 token 交织在一起,形成一个综合的多模态词汇表。语言 LLM 的原始词汇表包含 151,936 个条目,结合视觉码本和 6 个专门设计用于表示图像序列开始和结束的特殊 token 后,形成了一个 160,136 大小的多模态词汇表。在 MARS 的架构中,由 VQ-GAN 范式合成的视觉 token 与文本 token 享有同等地位。视觉词汇的初始嵌入是从预训练文本 token 的聚合均值嵌入中得出的,建立了跨模态集成的基础。